Salient Region Detection in outdoor scene using Imagery and 3-D Data
People
Publication
Gunhee Kim, Daniel Huber, and Martial Hebert
Segmentation of Salient Regions in Outdoor Scenes using Imagery and 3-D Data
IEEE Workshop on Application of Computer Vision (WACV 2008), Colorado, USA, January 7-9, 2008. (Oral)
[Paper(PDF)] [Presentation(PPT)]
Description
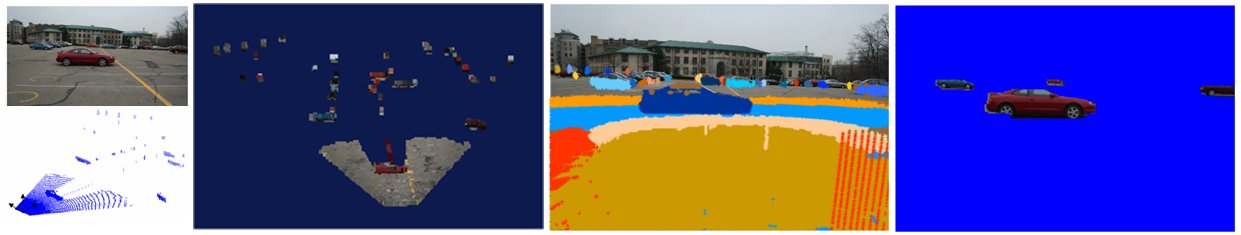
This project develops an algorithm for detecting and segmenting out the salient regions of a scene using both 3-D laser scan and imagery information. Fig.1 shows our problem statement. Given an image and its extrinsically calibrated 3-D scan data, our algorithm delineates top k-most salient regions in a bottom-up manner without any high-level priors, models, or learning.
The detection of salient clusters is formulated into finding the set of clusters that best fit some pre-defined families of probability density functions in 3-D scan data. Here we use two pdfs, which are Gaussian and Uniform. As a fundamental tool for this approach, we use the Robust Information-theoretic Clustering (RIC) method. After clustering, we calculate saliency value of each cluster by summing four different saliency features, which capture local, regional, and global properties of 3-D data and RGB color information.
Fig.2 shows some examples using the dataset taken in parking lots around CMU.
 |
 |
Funding
Robotics Consortium sponsored by the U.S Army Research Laboratory under the Collaborative Technology Alliance Program, Cooperative Agreement DAAD19-01-2-0012.